Difference between revisions of "Linden Lab Official:Map API"
Rand Linden (talk | contribs) |
Rand Linden (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
You can pan the map and zoom in and out. | You can pan the map and zoom in and out. | ||
=== Procedure === | ==== Procedure ==== | ||
To create this example, follow these steps: | To create this example, follow these steps: | ||
# Include required Javascript libraries. | # Include required Javascript libraries. | ||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
See the [[Webmap_API_Examples##Simple_map|Map API examples]] article for the complete example code. | See the [[Webmap_API_Examples##Simple_map|Map API examples]] article for the complete example code. | ||
=== Second Example: A Map with Markers === | === Second Example: A Map with Markers === | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 23 January 2009
We've made improvements and changes to the webmap, effective January 15, 2009.
Some information here may be out of date as we update this wiki with the changes. Thanks for your patience.
Getting Started
What is the Webmap API?
The Second Life Webmap API is a set of Javascript objects and functions that enable you to embed Second Life maps onto your web pages. If needed, you can also directly access the webmap images. Enough talk, lets jump into the code.
Disclaimer: This API is still in beta. URLs and API signatures may change. Check this page for announcements.
Prerequisites
To use the Second Life Webmap API, you must first:
- Sign up for a Google Maps API key. This enables you to use the Google Maps API, which is required to use SLMAPI. See the Google Maps API documentation for more information.
- Download prototype.js version 1.5.0.
- Download scriptaculous.js version 1.7.0.
- Download slmapapi.js. Alternatively, you can reference the online version in your pages; for example:
<script src="http://slurl.com/_scripts/slmapapi.js"><script>
About coordinates
Map coordinates are based on the Second Life grid system for positioning regions.
The Second Life world is mapped to the upper right quadrant of the world map as used by Google lat/long coordinates. A large scaling value called slGridEdgeSizeInRegions (equal to 220 or 1,048,576) defines the largest region coordinate at the top and far right edge of the displayed area. This value creates a map area with room for one trillion sims.
Diagram TBD.
The little xxx's in the diagram shows where the populated sims are in SL today.
About Zoom Levels
There are six zoom levels: one through six, one being the closest and six being the farthest. Each level zooms by a power of two. In other words, at zoom level five, each region is twice the width as it was at zoom level six.
Basic Examples
Simple map
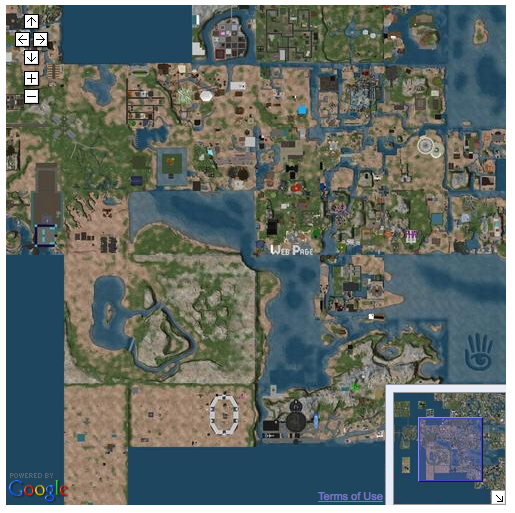
The first example is a map with basic panning and zooming capabilities. When you are done, it will look like this:
You can pan the map and zoom in and out.
Procedure
To create this example, follow these steps:
- Include required Javascript libraries.
- Include or reference the SLMAPAPI library.
- Add HTML body and div elements.
- Add Javascript onload event handler function.
- Save and test.
If you prefer, just copy all the code from Map API examples.
Include required Javascript libraries
Include the references to protoype.js and scriptaculous.js:
<script src="prototype.js" type="text/javascript"></script> <script src="scriptaculous/scriptaculous.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
Make sure both files are where you specify. Here, protoype.js is in the same directory as the example HTML file and scriptaculous.js is in a /scriptaculous subdirectory.
Next include the reference for the Google Maps API:
<script src="http://maps.google.com/maps?file=api&v=2&key={YOUR GOOGLE MAPS KEY GOES HERE}" type="text/javascript"></script>
Replace {YOUR GOOGLE MAPS KEY GOES HERE} with your Google Map key.
Include or reference the Webmap API library
Include the reference to the Second Life Map API Javascript file:
<script src="http://slurl.com/_scripts/slmapapi.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
If you prefer, download the file locally, and refer to it using a relative path.
Add HTML body and div elements
Next, add the HTML body containing div element to contain your map. The body contains a Javascript onload event handler that calls the loadmap() function you will define in the next step.
<body onload="loadmap()"> &tl;div id="map-container"></div> </body>
After the div element is passed to the map constructor, all that is left to do is to center the map and set the zoom.
NOTE: If you want the position attribute of the div element to be absolute, either set it programmatically via Javascript or using the style attribute tag. Setting the position attribute of this element in the CSS stylesheet will not work.
Add Javascript onload event handler function
Add the following Javascript function in the head of your page to instantiate the map and center it.
<script>
function loadmap() {
mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'));
mapInstance.centerAndZoomAtSLCoord(new XYPoint(1000,1000),3);
}
</script>
Save and test
When you are done, save the file, and then load it into your web browser. Try panning the map by clicking and dragging the mouse cursor; you can also pan by clicking on the arrow icons on the four sides. Also try zooming the view in and out by clicking the "+" and "-" icons.
See the Map API examples article for the complete example code.
Second Example: A Map with Markers
This example shows how to make a map with a marker. The code is the same as the first example, with extra lines of javascript added after the initialization of the map.
// creates the icons
var yellow_dot_image = new Img("b_map_yellow.gif",9,9);
var yellow_icon = new Icon(yellow_dot_image);
var all_images = [yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon];
// creates the marker
var marker = new Marker(all_images, new XYPoint(997,1002));
mapInstance.addMarker(marker);
The code above first creates the icon for the marker, then it to the map at (997, 1002) (where the Welcome Area Fountain is). Clicking on this marker does nothing, but read the following sections to find out how to do more.
Third Example: A Map with Windows
This example shows how to create a map a window. The code is the same as the first example, with extra lines of javascript added after the initialization of the map. In addition, the map is centered in a different location in order to make the window fully visible.
// creates a window
var mapWindow = new MapWindow("This is where the welcome area fountain is!!");
mapInstance.addMapWindow(mapWindow, new XYPoint(997,1002));
The code above adds an open window to the map positioned again at xxx.x, xxx.x, right above the Welcome Area Fountain. Note, after you close the window there is no way of bringing it back, unless you are using markers with windows. Read on to find out how to do this.
Fourth Example: Markers with Windows
This example shows how to create a map with a marker which opens a window when clicked. The code is a combination of the first, second and third examples. We have the following after we initialize the map:
// creates the icons
var yellow_dot_image = new Img("b_map_yellow.gif",9,9);
var yellow_icon = new Icon(yellow_dot_image);
var all_images = [yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon];
// creates the marker
var marker = new Marker(all_images, new XYPoint(997,1002));
mapInstance.addMarker(marker);
// creates a window
var mapWindow = new MapWindow("This is where the welcome area fountain is!! <br><img src='fountain.gif'>");
// adds the marker to the map
mapInstance.addMarker(marker, mapWindow);
The code above adds a marker and when clicked, opens an window. If the window is closed, it can be opened again by clicking on the marker again.
In these 4 examples we've shown you all the basic uses of the map. Yep, its really pretty simple if you ask us. If you want to read about some more advanced features of the map, you can read the next section.
Advanced Examples
Using Second Life Region Names (NOT IMPLEMENTED)
I know you've been wondering, what if I don't know which XY coordinate corresponds to which region name? Well, with this feature you can now use region names to define locations on the map instead of XY coordinates. If you'd like, skip to the example.
SLPoint('ahern',128,128); // use this instead of XYPoint(997,1002)
The above code simply creates an SLPoint located at the Welcome Area. Instead of having to figure out the XY coodinates, we were just able to use the region name. With this SLPoint now we can do whatever we want with it, like recenter the map here, put a window here, or put a marker here.
Note - The region name is case insensitive, so to specificy "Da Boom" region, you could use:
SLPoint("da boom") // OR
SLPoint("dA bOOm")
Linking to a Second Life Coordinate using XY Coordinates (NEW)
We've created an easy function to use in order to teleport your users to an absolute coordinate, for example 1000.5, 1000.5. If you'd like, skip to the example.
gotoSLURL(997,1002);
The above code will open up the Second Life client and then teleport the user to (997,1002) (where the welcome area fountain is).
Removing a Marker
Markers can be removed by passing the original marker to the removeMarker function. If you'd like, skip to the example.
mapInstance.removeMarker(marker);
The above code simply removes the marker, where marker is a reference to the original marker.
Removing Zoom and Pan Controls / Making your Own
If you'd like to remove all the panning and zooming controls, or would like to create your own, its all pretty easy. If you'd like, skip to the example.
mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'), {hasZoomControls: false, hasPanningControls: false});
The above code sets the map options hasZoomControls as false and hasPanControls as also false.
Now, if we'd like to create our own zoom and pan controls, its not that hard either. We have created functions setCurrentZoomLevel(), getCurrentZoomLevel(), zoomIn(), zoomOut, panLeft, panRight, panUp and panDown so that you can essentially skin your maps.
In our example we've created an anchored link for each function, which will call its respective function when it is clicked.
Disabling/Enabling Dragging
Say you'd like to disable dragging on the map. No problem. If you'd like, skip to the example.
mapInstance.disableDragging();
This one is simple, simply call disableDragging on the map object. When you are done just call enableDragging() on the map object to make it all normal again.
Panning or Recentering the Map
This feature will let you pan the map to a specific coordinate. If the coordinate is not currently visible on the map, the map will instead just recenter the map to this location. If you'd like, skip to the example.
mapInstance.panOrRecenterToSLCoord(new XYPoint(1000,1000), true);
The above code pans or recenters to (1000,1000) depending on the current view. The second parameter is optional, and if it is set to true, centers the map on the coordinate even if it is currently in the viewport.
Setting a Marker's Event Handlers
The following two features are pretty cool in our opinion. In a nutshell they'll allow you to do some interesting things. If you'd like, skip to the example.
Lets say you want to something else to happen besides a window opening when a marker is clicked. Like, for example, to retrieve a page about that specific coordinate or to show trigger some other javascript functionality you have on your page? Well, all this is possible.
// creates a function that we will bind to the marker click action
var doMarkerAction = function(marker) {
alert("an event occured at (" + marker.slCoord.x + "," + marker.slCoord.y + ")");
};
// creates the marker and sets its event handlers
var marker = new Marker(all_images, new XYPoint(997,1002), {clickHandler: doMarkerAction, onMouseOutHandler: doMarkerAction, onMouseOverHandler: doMarkerAction});
The code above simple sets the click handler, onmouseover, and onmouseout handlers of the marker to a function we've defined: doMarkerAction(). The marker is passed as a parameter to this function, so, if we want, we can remove it from the map, or just see what coordinate it lies on.
Setting a Double Click Handler
This feature of the map is very similar to the previous example, except it instead of the user having to click on a marker, he can click on anywhere on the map. Cool? Yes we think so. Heres an simpler example to look at.
// creates a function that we will bind to the double click action
var doubleClickHandlerFunction = function(x,y) {
alert("you double clicked at (" + x + "," + y + ")");
};
// creates the map
var mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'),{doubleClickHandler: doubleClickHandlerFunction});
mapInstance.centerAndZoomAtSLCoord(new XYPoint(997.5,1001.5),2);
The above code will fire off a javascript alert with the X and Y coordinate clicked. The X and Y coordinate will be passed as parameters to the function you specify to be the double click handler.
Similarly to the doubleClickHandler option, you can now set the singleClickHandler option. Please refer to this example
Setting a On State Changed Handler
Lets say whenever the user moves around or zooms on the map, we want to fire off some function. With the onStateChangedHandler option, we can set a handler function to be called whenever this happens. If you'd like, skip to the example.
mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'), {onStateChangedHandler: doSomething});
Whenever the state of the map changes, the doSomething function will be called. Hint: This feature is very handy when you only want to show markers currently in the user's viewport: whenever this handler is called, simply remove all the current markers, then grab a new set of markers to place on the map based on the current map bounds.
Triggering a Marker Click
This feature simulates clicking a certain marker. If the marker currently isn't in the map viewport, it will recenter the map to this coordinate. If you'd like, skip to the example.
mapInstance.clickMarker(marker);
Tips: This feature can come in handy if you are listing links somewhere else on the page, and want links to open up markers with more information.
Get Current Map Center / Map Bounds
These features will let you see where the map is currently centered and what the current bounds of the map are. If you'd like, skip to the example.
var bounds = mapInstance.getViewportBounds(); var center = mapInstance.getMapCenter();
The getCodeBounds function will return a Bounds object, which basically contains xMin, xMax, yMin, and yMax attributes of the current viewport. The getMapCenter function will return an XYPoint object representing the center of the map.
Tips: We can imagine this feature would be handy if you were only showing markers inside the current map viewport, or showing markers based on the proximity from the map center.
Using PNG Images and Shadows with Markers
You can also use PNG Images to make your icons even more pretty. If you'd like, skip to the example.
// creates the icons
var forsale_sign = new Img("forsale.png",80,83, true); // note how the fourth parameter is set true!
var forsale_shadow = new Img("forsale-shadow.png",98,83, true);
var forsale_icon = new Icon(forsale_sign, forsale_shadow);
var all_images = [forsale_icon, forsale_icon, forsale_icon, forsale_icon, forsale_icon, forsale_icon];
// creates the marker
var marker = new Marker(all_images, new XYPoint(995,1004));
mapInstance.addMarker(marker);
The above code is almost identical to example two, except that when we define an Img, we specify a fourth argument in the constructor, telling the class to create the image with an alpha channel (alpha channel basically means that fancy transparency you cant get with GIF's). Also, when we create the Icon, we also specify another Img as the second argument, which specifies a shadow. Thats pretty much all you have to do to get pretty PNG icons.
Setting Marker and Window Options
There are a variety of window options you can set. Please refer to the API Classes and Methods page for a complete explanation.
Accessing map images directly
You can also access the map images directly by reading them from the Amazon S3 servers.
The file format:
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/Z/XXXXX/YYYYY/map-Z-X-Y-objects.jpg
Z = Zoom level desired. 1 is always the most zoomed in view, meaning individual region tiles. The current max/world zoom is 8.
X,Y = The X and Y coordinates on the SL Grid of the region. Ex: region Ahern = (997,1002).
The directory names are padded to 5 characters with leading zeros.
Tiles with zoom greater than 1 are stored at the lower left corner coordinate of the tiles that are included in the image. In other words, you can find the zoom tile containing region /1/X/Y for zoom level Z at /Z/X - (X % Z)/Y - (Y % Z)
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/2/00498/00804/map-2-498-804-objects.jpg
Example: if zoom = 2, the 4 region tiles with filenames:
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/1/01000/01000/map-1-1000-1000-objects.jpg
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/1/01001/01000/map-1-1001-1000-objects.jpg
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/1/01000/01001/map-1-1000-1001-objects.jpg
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/1/01001/01001/map-1-1001-1001-objects.jpg
are compressed into the single tile:
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/2/01000/01000/map-2-1000-1000-objects.jpg
Other Examples:
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/8/01024/00896/map-8-1024-896-objects.jpg Zoomed all the way out - tile from full world view
http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/1/01027/01019/map-1-1027-1019-objects.jpg (A single tile contained in the view above, zoomed all the way in)
Where do I go from here?
With this new api in hand, we build something really cool. We've tried to develop with the idea that everything we can do, you should be able to do as well.
While we've developed this API around features we think we would need, we do understand there is always room for improvement. So, if you encounter problems or bugs, have feature requests for new api methods, or have something really cool to show us, please email webmap@secondlife.com.
Happy coding from the Second Life Web team.
Browser Compatibility
The map has been tested to work in Internet Explorer 6.0, Internet Explorer 7.0, Firefox 1.0 or greater and Safari 2.0. Other browsers may work but little issues may appear. Unless otherwise noted, all features work in all supported browsers.