Difference between revisions of "Linden Lab Official:Map API"
Rand Linden (talk | contribs) |
Rand Linden (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
* [http://www.google.com/apis/maps/signup.html Sign up for a Google Maps API key]. This enables you to use the Google Maps API, which is required to use SLMAPI. See the [http://code.google.com/apis/maps/documentation/ Google Maps API documentation] for more information. | * [http://www.google.com/apis/maps/signup.html Sign up for a Google Maps API key]. This enables you to use the Google Maps API, which is required to use SLMAPI. See the [http://code.google.com/apis/maps/documentation/ Google Maps API documentation] for more information. | ||
* Add the [[ | * Add the [[#Common_HTML_header|common header code]] at the beginning of each HTML file. This code loads the Google Maps and Webmap Javascript libraries, the Webmap cascading stylesheet (CSS), and some other basic code. | ||
NOTE: In general, it is best to reference the Webmap API Javascript library and CSS files that are on http://slurl.com. Although you can download these files locally and modify them for your own use, if Linden Lab updates or changes these files, your applications will not get the benefit and may even stop working properly. | NOTE: In general, it is best to reference the Webmap API Javascript library and CSS files that are on http://slurl.com. Although you can download these files locally and modify them for your own use, if Linden Lab updates or changes these files, your applications will not get the benefit and may even stop working properly. | ||
=== Common HTML header === | |||
To use the Webmap API, put the following lines at the beginning of each HTML page. This includes: | |||
* Statements to load the required Second Life Webmap API and Google Maps Javascript libraries. | |||
* Link to the Webmap cascading style sheet. | |||
* Style declaration for the map div element. This defines the size and other layout attributes of the map display. | |||
<pre> | |||
<html> | |||
<head> | |||
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1"> | |||
<script src="http://maps.google.com/maps?file=api&v=2&key={GOOGLE MAPS KEY}" | |||
type="text/javascript"></script> | |||
<script src="http://slurl.com/_scripts/slmapapi.js" type="text/javascript"></script> | |||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://slurl.com/_styles/MAIN.css" /> | |||
<style> | |||
div#map-container { | |||
width: 500px; | |||
height: 500px; | |||
} | |||
</style> | |||
... | |||
</pre> | |||
Replace {GOOGLE MAPS KEY} with you Google Maps Key. | |||
All the examples also require additional script statements in the HTML header. | |||
'''Stylesheet''' | |||
To use your own stylesheet, just include it AFTER the Webmap CSS, for example: | To use your own stylesheet, just include it AFTER the Webmap CSS, for example: | ||
| Line 45: | Line 76: | ||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="myStyleSheet.css" /> | <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="myStyleSheet.css" /> | ||
'''Body element''' | |||
Use the following body element in your HTML document: | |||
<body load="loadmap()" onunload="GUnload();"> | |||
... | |||
The '''GUnload()''' function is a Google Maps API function that reduces memory leaks, particularly with Internet Explorer. For more information, see the [http://code.google.com/apis/maps/documentation/#Memory_Leaks Google Maps API documentation]. | |||
=== Browser compatibility === | === Browser compatibility === | ||
| Line 82: | Line 108: | ||
* [[Webmap_API_Reference#MapWindow|Window]] - represents a captioned balloon pointing to a specified map location. | * [[Webmap_API_Reference#MapWindow|Window]] - represents a captioned balloon pointing to a specified map location. | ||
* [[Webmap_API_Reference#Img|Img]] and [[Webmap_API_Reference#Icon|Icon]] - represent an image to use for markers, controls, or in windows. | * [[Webmap_API_Reference#Img|Img]] and [[Webmap_API_Reference#Icon|Icon]] - represent an image to use for markers, controls, or in windows. | ||
===About coordinates=== | |||
Map coordinates are based on the Second Life grid system for positioning regions. | |||
[[Image:Webmap coords.jpg]] | |||
As illustrated in the diagram above, the Webmap API maps the Second Life world to the upper right quadrant of the Google world map. A large scaling value | |||
called slGridEdgeSizeInRegions (equal to 2<sup>20</sup> or 1,048,576) defines the largest region coordinate at the top and far right edge of the displayed area. This value creates a map area with room for one trillion sims. | |||
The little blue square illustrates where the populated sims are in Second Life. | |||
=== Zoom levels === | |||
There are eight zoom levels: one through eight, one being the closest and eight being the farthest. Each level zooms by a power of two. In other words, at zoom level five, each region is twice the width as it was at zoom level six. | |||
== Basic Examples == | == Basic Examples == | ||
| Line 118: | Line 158: | ||
|https://wiki.secondlife.com/w/images/d/d9/Forsale-shadow.png | |https://wiki.secondlife.com/w/images/d/d9/Forsale-shadow.png | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Simple map === | === Simple map === | ||
| Line 175: | Line 178: | ||
'''1. Add common HTML header''' | '''1. Add common HTML header''' | ||
First, include the [[Webmap_API#Common_HTML_header|common header code]], required by all Webmap applications. | First, include the [[Webmap_API#Common_HTML_header|common header code]], required by all Webmap applications. | ||
<pre><nowiki> | <pre><nowiki> | ||
Revision as of 00:05, 1 February 2009
We've made improvements and changes to the webmap, effective January 15, 2009.
Some information here may be out of date as we update this wiki with the changes. Thanks for your patience.
Getting Started
Second Life Webmap features and SLURLs
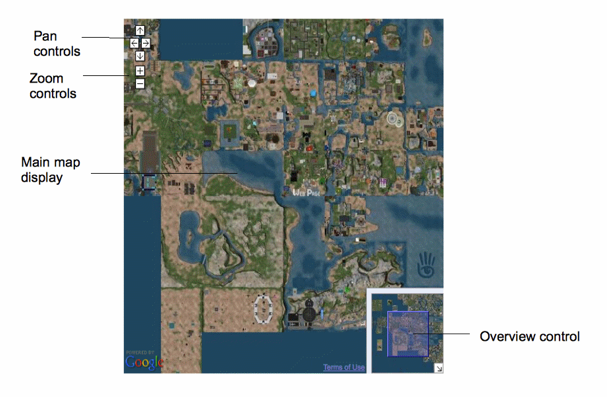
The Webmap API enables you to create web pages that have Google Maps functionality, using maps of Second Life, rather than Earth. In general, the default Webmap interface looks like the diagram at right.
The main map display area shows the current map area. By default, the map provides the following features:
- Click anywhere on the map to open a "teleport" window that displays the name of the region where you clicked and a button you can click to launch Second Life and teleport to that location.
- Click and drag the mouse pointer to pan the map view up, down, left, and right. If desired, you can disable this behavior.
- Double-click to zoom in by one level (power of two) and display the teleport window.
- Use the mouse wheel to zoom in and out. See Zoom levels for more information about zoom levels.
- Use the zoom and pan controls at upper left to zoom the view in and out and to pan the view up, down, left, and right. If desired, you can easily create your own custom zoom and pan controls.
- Use the overview control to move the view around by clicking and dragging, or double-clicking. Close the overview control by clicking on the diagonal arrow at the very bottom right of the map. You can specify whether the map provides an overview control when you create the map object.
The website http://slurl.com uses the Webmap API to provide a mechanism for teleporting to locations in Second Life from web pages.
What is the Webmap API?
The Second Life Webmap API is a set of Javascript objects and functions that enable you to embed Second Life maps onto your web pages. It is a purely client-side Javascript API. If needed, you can also directly access the webmap images.
NOTE: This API is still in beta. URLs and API signatures may change.
Prerequisites
To use the Second Life Webmap API in a web page, you must first:
- Sign up for a Google Maps API key. This enables you to use the Google Maps API, which is required to use SLMAPI. See the Google Maps API documentation for more information.
- Add the common header code at the beginning of each HTML file. This code loads the Google Maps and Webmap Javascript libraries, the Webmap cascading stylesheet (CSS), and some other basic code.
NOTE: In general, it is best to reference the Webmap API Javascript library and CSS files that are on http://slurl.com. Although you can download these files locally and modify them for your own use, if Linden Lab updates or changes these files, your applications will not get the benefit and may even stop working properly.
Common HTML header
To use the Webmap API, put the following lines at the beginning of each HTML page. This includes:
- Statements to load the required Second Life Webmap API and Google Maps Javascript libraries.
- Link to the Webmap cascading style sheet.
- Style declaration for the map div element. This defines the size and other layout attributes of the map display.
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1">
<script src="http://maps.google.com/maps?file=api&v=2&key={GOOGLE MAPS KEY}"
type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="http://slurl.com/_scripts/slmapapi.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://slurl.com/_styles/MAIN.css" />
<style>
div#map-container {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
}
</style>
...
Replace {GOOGLE MAPS KEY} with you Google Maps Key.
All the examples also require additional script statements in the HTML header.
Stylesheet
To use your own stylesheet, just include it AFTER the Webmap CSS, for example:
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://slurl.com/_styles/MAIN.css" /> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="myStyleSheet.css" />
Body element
Use the following body element in your HTML document:
<body load="loadmap()" onunload="GUnload();"> ...
The GUnload() function is a Google Maps API function that reduces memory leaks, particularly with Internet Explorer. For more information, see the Google Maps API documentation.
Browser compatibility
The Webmap API has been tested to work with the following browsers:
- Internet Explorer 6.0
- Internet Explorer 7.0
- Firefox 1.0 or greater
- Safari 2.0
Other browsers may work but little issues may appear. Unless otherwise noted, all features work in all supported browsers.
Comments and feedback
If you encounter problems or bugs or have feature requests, please email webmap@secondlife.com.
Happy coding from the Second Life Web team!
Basic concepts
The Webmap API's fundamental class is SLMap. It is a Javascript object representing the map with a large number of methods, enabling you to zoom, pan the view, and so on.
Additionally, the API includes the following key classes:
- Marker - represents an image to display at a specify (x,y) point on the map. You provide a set of images to display at each zoom level. Contains several event handlers and other properties.
- Window - represents a captioned balloon pointing to a specified map location.
- Img and Icon - represent an image to use for markers, controls, or in windows.
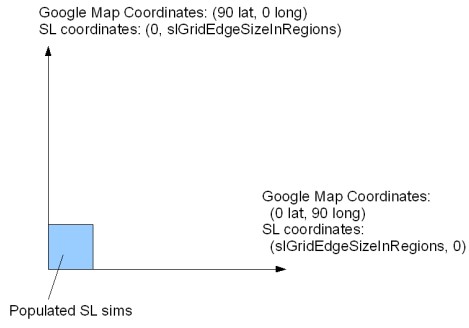
About coordinates
Map coordinates are based on the Second Life grid system for positioning regions.
As illustrated in the diagram above, the Webmap API maps the Second Life world to the upper right quadrant of the Google world map. A large scaling value called slGridEdgeSizeInRegions (equal to 220 or 1,048,576) defines the largest region coordinate at the top and far right edge of the displayed area. This value creates a map area with room for one trillion sims.
The little blue square illustrates where the populated sims are in Second Life.
Zoom levels
There are eight zoom levels: one through eight, one being the closest and eight being the farthest. Each level zooms by a power of two. In other words, at zoom level five, each region is twice the width as it was at zoom level six.
Basic Examples
Required image files
Some of the following examples use image files for markers. To run the examples with the code as shown, download the image files and save them in the same directory as the example HTML files. Alternatively, create the Img objects using the URLs listed in the table below that refer to the images stored on this wiki.
The following table lists the images used in the examples:
| Image | File name | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Yellow marker.gif | https://wiki.secondlife.com/w/images/2/23/Yellow_marker.gif
| |

|
Fountain.gif | https://wiki.secondlife.com/w/images/6/60/Fountain.gif |

|
Forsale.png | https://wiki.secondlife.com/wiki/Image:Forsale.png |

|
Forsale-shadow.png | https://wiki.secondlife.com/w/images/d/d9/Forsale-shadow.png |
Simple map
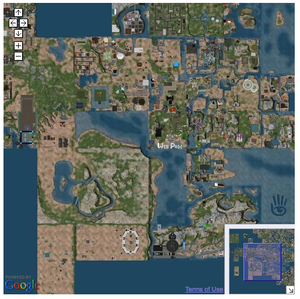
The first example is a map with basic panning and zooming capabilities. When you are done, it will look as shown here.
You can pan the map and zoom in and out.
To create this example, follow these steps:
- Add common HTML header code.
- Add HTML body element.
- Add loadmap() function.
- Save and test.
1. Add common HTML header
First, include the common header code, required by all Webmap applications.
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1">
<script src="http://slurl.com/_scripts/slmapapi.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="http://maps.google.com/maps?file=api&v=2&key={GOOGLE MAPS KEY}" type="text/javascript"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://slurl.com/_styles/MAIN.css" />
<style>
div#map-container {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
}
</style>
...
</head>
Be sure to replace {GOOGLE MAPS KEY} with your Google Map key.
2. Add HTML body element
Next, add the HTML body element to contain your map. The body contains a Javascript onload event handler that calls the loadmap() function you will define in the next step.
<body onload="loadmap()" onunload="GUnload()"> <div id="map-container"></div> </body>
The div element is passed to the SLMap object constructor, using the document.getElementById('map-container') DOM method call.
NOTE: If you want the position attribute of the div element to be absolute, either set it programmatically using Javascript or using the style attribute tag. Setting the position attribute of this element in the CSS stylesheet will not work.
3. Add loadmap() function
The body element you just added has a Javascript event handler for the "onload" event, called when the browser initially loads the page. You deifined this to call a loadmap() function. Now, define that Javascript function in the head of your page (after the code that is already there), as follows:
<script>
function loadmap() {
mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'));
mapInstance.centerAndZoomAtSLCoord(new XYPoint(997, 1002), 3);
}
</script>
The first line defines a new Map object from the HTML div element. The second line centers the map at a specific point, and zooms it to zoom level three.
4. Save and test
When you are done, save the file, and then load it into your web browser. Try panning the map by clicking and dragging the mouse cursor; you can also pan by clicking on the arrow icons on the four sides. Also try zooming the view in and out by clicking the "+" and "-" icons.
Complete source code
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1">
<script src="http://maps.google.com/maps?file=api&v=2&key=[GOOGLE MAPS KEY]" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="http://slurl.com/_scripts/slmapapi.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://slurl.com/_styles/MAIN.css" />
<style>
div#map-container {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
}
</style>
<script>
function loadmap() {
mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'));
mapInstance.centerAndZoomAtSLCoord(new XYPoint(997, 1002), 2);
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="loadmap()" onunload="GUnload()">
<div id="map-container"></div>
</body>
Map with a marker
A marker is simply an image displayed at a specific location on the map. The Webmap API enables you to define an image for each zoom level, so the marker can appear differently at each zoom level if you wish.
This example shows how to make a map with a marker. The code is the same as the first example, with with addition of some Javascript after the initialization of the map in the page's onload event handler function, loadmap().
To use the code below verbatim, you must download the marker image as described in Required image files; you can also use the URL of the wiki image if you prefer.
The code first creates the icon for the marker, then places it on the map at (997, 1002) at the welcome area fountain. Because the same icon is specified for every zoom level, it appears the same size regardless of zoom level.
// Create the icons
var yellow_dot_image = new Img("Yellow_marker.gif", 9, 9);
var yellow_icon = new Icon(yellow_dot_image);
var all_images = [yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon];
// Create the marker
var marker = new Marker(all_images, new XYPoint(997, 1002));
mapInstance.addMarker(marker);
In this example, clicking on the marker does nothing. Subsequent examples illustrate adding some onClick behavior.
Source code
Replace the first line comment below with the common header code.
<!-- Insert common HTML header -->
<script>
function loadmap() {
// creates the map
var mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'));
mapInstance.centerAndZoomAtSLCoord(new XYPoint(997, 1002), 2);
// creates the icons
var yellow_dot_image = new Img("Yellow_marker.gif", 9, 9);
var yellow_icon = new Icon(yellow_dot_image);
var all_images = [yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon];
// creates the marker
var marker = new Marker(all_images, new XYPoint(997, 1002));
mapInstance.addMarker(marker);
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="loadmap()" onunload="GUnload()">
<p>There should be a yellow marker in the center of this map:
<div id="map-container"></div>
</body>
Map with an initial open window
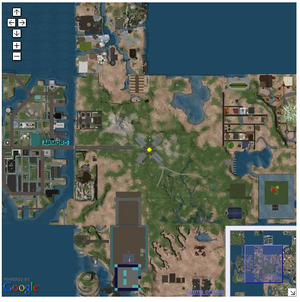
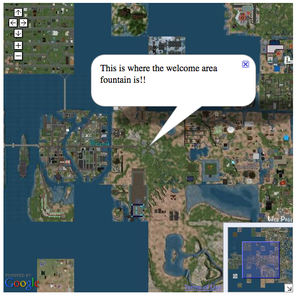
A Webmap window is a caption pointing to a specific point on the map, as shown in the screenshot at right. It looks something like a comic book dialog bubble.
Use the MapWindow object to create a window. For example, to create a window that opens initially when the page loads:
- Instantiate a MapWindow object with the desired caption.
- Call the addMapWindow() method on the SLMap object to add the window to the map.
For example:
// creates a window
var mapWindow = new MapWindow("This is where the welcome area fountain is!!");
mapInstance.addMapWindow(mapWindow, new XYPoint(997, 1002));
The code adds an open window to the map positioned again at (997, 1002), right above the welcome area fountain.
NOTE: after the user closes the window there is no way to bring it back. A subsequent example will show how to enable the user to reopen the window, by using markers with windows.
To make the map initially centered on the fountain, change the call to centerAndZoomAtSLCoord() as follows:
mapInstance.centerAndZoomAtSLCoord(new XYPoint(997, 1002), 3);
Source code
This example shows how to create a map with a window. The code is the same as the first example, with the addition of some lines of Javascript after the initialization of the map, in the loadmap() function. In addition, the map is centered in a different location in order to make the window fully visible.
Replace the first line comment below with the common header code.
<!-- Insert common HTML header -->
<script>
function loadmap() {
mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'));
mapInstance.centerAndZoomAtSLCoord(new XYPoint(997, 1002), 3);
// Create window
var mapWindow = new MapWindow("This is where the welcome area fountain is!!");
mapInstance.addMapWindow(mapWindow, new XYPoint(997, 1002));
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="loadmap()" onunload="GUnload()">
<h1>Simple Map Example</h1>
<div id="map-container"></div>
</body>
Map with a marker that opens a windows
This example shows how to create a map with a marker which opens a window when clicked. It is a combination of the previous two examples, because the code first creates a marker and a window.
The difference comes in adding the marker to the map: this time you provide the window object as well as the marker object in the call to addMarker():
mapInstance.addMarker(marker, mapWindow);
Doing this adds the marker and causes it to open the specified window when the user clicks it. If the user subsequently closes the window, s/he can open it again by clicking on the marker.
Source code
Replace the first line comment below with the common header code.
<!--- Insert common HTML header --->
<script>
function loadmap() {
// Create the map
var mapInstance = new SLMap(document.getElementById('map-container'));
mapInstance.centerAndZoomAtSLCoord(new XYPoint(997.5, 1001.5), 2);
// Create the icons
var yellow_dot_image = new Img("Yellow_marker.gif", 9, 9);
var yellow_icon = new Icon(yellow_dot_image);
var all_images = [yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon, yellow_icon];
// Create the marker
var marker = new Marker(all_images, new XYPoint(997, 1002));
// Create a window
var mapWindow = new MapWindow("This is where the welcome area fountain is!! <br><img src='Fountain.gif'>");
// Adds the marker to the map
mapInstance.addMarker(marker, mapWindow);
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="loadmap()" onunload="GUnload()">
<p>This map shows a yellow marker on the welcome fountain. When you click the marker,
a window appears with a screenshot of the fountain.</p>
<div id="map-container"></div>
</body>
Accessing map images directly
The Second Life map images are stored on Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3). You can access the map images directly on the Amazon S3 servers using the following URL format:
http://map.secondlife.com/Z/XXXXX/YYYYY/map-Z-X-Y-objects.jpg
Where:
- Z - Zoom level desired:
- One (1) is the most zoomed-in view, showing individual region tiles.
- Eight (8) is the maximum zoom level, showing the entire world.
- X,Y - X and Y coordinates on the Second Life Grid of the region, for example, region Ahern is (997,1002). In the "directory path" (not the file name), pad the coordinate values to five characters with leading zeros; so for the previous coordinates, the path would be "00997/01002".
Tiles with zoom greater than one are stored at the lower left corner coordinate of the tiles that are included in the image. In other words, you can find the zoom tile containing region (X,Y) for zoom level Z at the directory Z/X'/Y' where:
X' = X - (X % (2Z - 1) )
and
Y' = Y - (Y % (2Z - 1) )
Note that 2Z - 1 is the number of regions encompassed by the width of a tile at resolution Z.
Examples
For example: if Z = 2, the four region tiles are:
- http://map.secondlife.com/1/01000/01000/map-1-1000-1000-objects.jpg
- http://map.secondlife.com/1/01001/01000/map-1-1001-1000-objects.jpg
- http://map.secondlife.com/1/01000/01001/map-1-1000-1001-objects.jpg
- http://map.secondlife.com/1/01001/01001/map-1-1001-1001-objects.jpg
These four region tiles are compressed into the single tile:
http://map.secondlife.com/2/01000/01000/map-2-1000-1000-objects.jpg
The following shows the map zoomed all the way out, showing the entire Second Life world view: http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/8/01024/00896/map-8-1024-896-objects.jpg
The following displays a single tile contained in the view above, zoomed all the way in: http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/1/01027/01019/map-1-1027-1019-objects.jpg
Getting a map URL from LSL
The following LSL script illustrates how to display a map of the current region to an avatar:
<lsl> ShowMap(key avatar) {
string url = "http://map.secondlife.com.s3.amazonaws.com/1/"; vector sim_coord = llGetRegionCorner(); string x = (string)((integer)(sim_coord.x / 256.0)); string y = (string)((integer)(sim_coord.y / 256.0)); string x0 = llStringTrim(llGetSubString(" 00000", 0, 5 - llStringLength(x)), STRING_TRIM_HEAD) + x; string y0 = llStringTrim(llGetSubString(" 00000", 0, 5 - llStringLength(y)), STRING_TRIM_HEAD) + y; url += x0 + "/" + y0 + "/" + "map-1-" + x + "-" + y + "-objects.jpg"; llLoadURL(avatar, "View the sim map", url);
} </lsl>
Contributed under GPL v3 license by Henri Beauchamp 09:00, 24 January 2009 (UTC)