Difference between revisions of "Interpolation"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Float Linear | ====Float Linear==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Float Cosine | ====Float Cosine==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Cosine interpolation of f0 and f1 with fraction t. | Cosine interpolation of f0 and f1 with fraction t. | ||
<lsl> | <lsl> | ||
float fCos(float | float fCos(float f0,float f1,float t) { | ||
float F = (1 - llCos(t*PI))/2; | float F = (1 - llCos(t*PI))/2; | ||
return | return f0*(1-F)+f1*F; | ||
} | } | ||
</lsl> | </lsl> | ||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Float Cubic | ====Float Cubic==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Float Hermite | ====Float Hermite==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Float Cubic Catmull-Rom | ====Float Cubic Catmull-Rom==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 226: | Line 226: | ||
!style="background-color: #d0d0ee" | Description | !style="background-color: #d0d0ee" | Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rotation <float f0, float f1, float f2, float f3> | | rotation H | ||
| <float f0, float f1, float f2, float f3> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| float t | | float t | ||
| Line 247: | Line 248: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Float Rescale | ====Float Rescale==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 292: | Line 293: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Float Rescale Fixed | ====Float Rescale Fixed==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 299: | Line 300: | ||
float fSclFix( float from0, float from1, float to0, float to1, float t ) { | float fSclFix( float from0, float from1, float to0, float to1, float t ) { | ||
t = to0 + ( (to1 - to0) * ( (from0 - t) / (from0-from1) ) ); | t = to0 + ( (to1 - to0) * ( (from0 - t) / (from0-from1) ) ); | ||
if(t < to0) t = to0; else if(t > to1) t = to1; return t; } | if(t < to0) t = to0; else if(t > to1) t = to1; return t; | ||
} | |||
</lsl> | </lsl> | ||
| Line 334: | Line 336: | ||
By Nexii Malthus</div> | By Nexii Malthus</div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
<!--############# FLOAT TARGET ###############--> | |||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | |||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | |||
====Float Target==== | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
Steps float 'Now' closer using float 'Vel' towards 'Target' while clamping between 'Min' and 'Max'. Useful for games, simulations and vehicles. For example keeping realtime track of linear and angular acceleration and velocity of a vehicle. | |||
<lsl> | |||
float fTarget(float Now, float Target, float Min, float Max, float Vel) { | |||
if(llFabs(Target-Now) < Vel) return Target; | |||
if(Now < Target) Now += Vel; else Now -= Vel; | |||
if(Now < Min) Now = Min; else if(Now > Max) Now = Max; | |||
return Now; | |||
} | |||
</lsl> | |||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | |||
| | |||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="6" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #e0e0ff; border-collapse: collapse" | |||
!style="background-color: #d0d0ee" | Input | |||
!style="background-color: #d0d0ee" | Description | |||
|- | |||
| float Now | |||
| 'Now' current value | |||
|- | |||
| float Target | |||
| move 'Now' towards 'Target' | |||
|- | |||
| float Min | |||
| Clamp output at minimum | |||
|- | |||
| float Max | |||
| Clamp output at maximum | |||
|- | |||
| float Vel | |||
| Move 'Now' towards 'Target' at 'Vel' (Velocity) | |||
|- | |||
!style="background-color: #d0d0ee" | Output | |||
!style="background-color: #d0d0ee" | Description | |||
|- | |||
| return float fTarget | |||
| Returns clamped output of a single step of 'Now' towards 'Target' using 'Vel' | |||
|} | |||
| Graph goes here, k. | |||
|} | |||
<div style="float:right;font-size: 80%;"> | |||
By Nexii Malthus</div> | |||
|} | |||
=== Vector Functions === | === Vector Functions === | ||
| Line 340: | Line 393: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Vector Linear | ====Vector Linear==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 379: | Line 432: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Vector Cosine | ====Vector Cosine==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 419: | Line 472: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Vector Cubic | ====Vector Cubic==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 465: | Line 518: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Vector Hermite | ====Vector Hermite==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 527: | Line 580: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Rotation Linear | ====Rotation Linear==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 570: | Line 623: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Rotation Cosine | ====Rotation Cosine==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 614: | Line 667: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Rotation Cubic | ====Rotation Cubic==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 668: | Line 721: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Vector List, Linear | ====Vector List, Linear==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 722: | Line 775: | ||
{|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | {|cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="1" style="border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0pt; background-color: #ffffff; border-collapse: collapse" width="80%" | ||
!style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | !style="color: #000000; background-color: #aaaaff;" height="20px"| | ||
Rotation Cosine Aim | ====Rotation Cosine Aim==== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Revision as of 12:44, 4 September 2011
| LSL Portal | Functions | Events | Types | Operators | Constants | Flow Control | Script Library | Categorized Library | Tutorials |
Interpolation Library
Float Functions
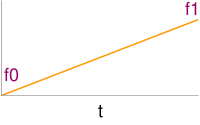
Float Linear | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Linear interpolation of f0 and f1 with fraction t. <lsl> float fLin(float f0,float f1,float t) { return f0*(1-t) + f1*t; } </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
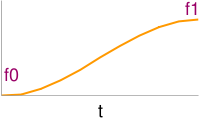
Float Cosine | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cosine interpolation of f0 and f1 with fraction t. <lsl> float fCos(float f0,float f1,float t) { float F = (1 - llCos(t*PI))/2; return f0*(1-F)+f1*F; } </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
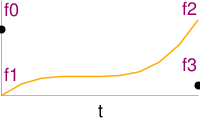
Float Cubic | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cubic interpolation of f0, f1, f2 and f3 with fraction t. <lsl> float fCub(float f0,float f1,float f2,float f3,float t) { float P = (f3-f2)-(f0-f1);float Q = (f0-f1)-P;float R = f2-f0;float S = f1; return P*llPow(t,3) + Q*llPow(t,2) + R*t + S; } </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Float Hermite | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Hermite interpolation of f0, f1, f2 and f3 with fraction t, tension and bias. <lsl> float fHem(float f0,float f1,float f2,float f3,float t,float tens,float bias){ float t2 = t*t;float t3 = t2*t;
float a0 = (f1-f0)*(1+bias)*(1-tens)/2;
a0 += (f2-f1)*(1-bias)*(1-tens)/2;
float a1 = (f2-f1)*(1+bias)*(1-tens)/2;
a1 += (f3-f2)*(1-bias)*(1-tens)/2;
float b0 = 2*t3 - 3*t2 + 1;
float b1 = t3 - 2*t2 + t;
float b2 = t3 - t2;
float b3 = -2*t3 + 3*t2;
return ( b0 * f1+b1 * a0+b2 * a1+b3 * f2 );
} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Float Cubic Catmull-Rom | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Catmull-Rom cubic interpolation spline of four floats with fraction t. The four floats are stored in a compact rotation format. <lsl> rotation mCat1 = <-0.5, 1.0, -0.5, 0.0>; rotation mCat2 = < 1.5, -2.5, 0.0, 1.0>; rotation mCat3 = <-1.5, 2.0, 0.5, 0.0>; rotation mCat4 = < 0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 0.0>; float fCatmullRom(rotation H, float t) { rotation ABCD = <
(H.x * mCat1.x) + (H.y * mCat2.x) + (H.z * mCat3.x) + (H.s * mCat4.x),
(H.x * mCat1.y) + (H.y * mCat2.y) + (H.z * mCat3.y) + (H.s * mCat4.y),
(H.x * mCat1.z) + (H.y * mCat2.z) + (H.z * mCat3.z) + (H.s * mCat4.z),
(H.x * mCat1.s) + (H.y * mCat2.s) + (H.z * mCat3.s) + (H.s * mCat4.s)
>;
rotation T; T.s = 1.0; T.z = t; T.y = T.z*T.z; T.x = T.y*T.z;
return T.x*ABCD.x + T.y*ABCD.y + T.z*ABCD.z + T.s*ABCD.s;
} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Float Rescale | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rescales a value from one range to another range. <lsl> float fScl( float from0, float from1, float to0, float to1, float t ) { return to0 + ( (to1 - to0) * ( (from0 - t) / (from0-from1) ) ); } </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Float Rescale Fixed | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rescales a value from one range to another range. The value is clamped between the range. <lsl> float fSclFix( float from0, float from1, float to0, float to1, float t ) { t = to0 + ( (to1 - to0) * ( (from0 - t) / (from0-from1) ) ); if(t < to0) t = to0; else if(t > to1) t = to1; return t; } </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Float Target | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Steps float 'Now' closer using float 'Vel' towards 'Target' while clamping between 'Min' and 'Max'. Useful for games, simulations and vehicles. For example keeping realtime track of linear and angular acceleration and velocity of a vehicle. <lsl> float fTarget(float Now, float Target, float Min, float Max, float Vel) { if(llFabs(Target-Now) < Vel) return Target; if(Now < Target) Now += Vel; else Now -= Vel; if(Now < Min) Now = Min; else if(Now > Max) Now = Max; return Now; } </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Vector Functions
Vector Linear | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Linear interpolation of v0 and v1 with fraction t. <lsl> vector vLin(vector v0, vector v1,float t){ return v0*(1-t) + v1*t;} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Vector Cosine | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cosine interpolation of v0 and v1 with fraction t. <lsl> vector vCos(vector v0,vector v1,float t){ float F = (1 - llCos(t*PI))/2; return v0*(1-F)+v1*F;} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Vector Cubic | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cubic interpolation of v0, v1, v2 and v3 with fraction t. <lsl> vector vCub(vector v0,vector v1,vector v2,vector v3,float t){ vector P = (v3-v2)-(v1-v0);vector Q = (v1-v0)-P;vector R = v2-v1;vector S = v0; return P*llPow(t,3) + Q*llPow(t,2) + R*t + S;} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Vector Hermite | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Hermite interpolation of v0, v1, v2 and v3 with fraction t, tension and bias. <lsl> vector vHem(vector v0,vector v1,vector v2,vector v3,float t,float tens,float bias){ float t2 = t*t;float t3 = t2*t;
vector a0 = (v1-v0)*(1+bias)*(1-tens)/2;
a0 += (v2-v1)*(1-bias)*(1-tens)/2;
vector a1 = (v2-v1)*(1+bias)*(1-tens)/2;
a1 += (v3-v2)*(1-bias)*(1-tens)/2;
float b0 = 2*t3 - 3*t2 + 1;
float b1 = t3 - 2*t2 + t;
float b2 = t3 - t2;
float b3 = -2*t3 + 3*t2;
return ( b0 * v1+b1 * a0+b2 * a1+b3 * v2 );}
</lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Rotation Functions
Rotation Linear | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Spherical Linear interpolation of r0 and r1 with fraction t. Also known as SLERP <lsl> rotation rLin(rotation r0,rotation r1,float t){ // Spherical-Linear Interpolation float ang = llAngleBetween(r0, r1); if( ang > PI) ang -= TWO_PI; return r0 * llAxisAngle2Rot( llRot2Axis(r1/r0)*r0, ang*t);} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Rotation Cosine | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Spherical Cosine interpolation of r0 and r1 with fraction t. I liken to call it as SCORP <lsl> rotation rCos(rotation r0,rotation r1,float t){ // Spherical-Cosine Interpolation float f = (1 - llCos(t*PI))/2; float ang = llAngleBetween(r0, r1); if( ang > PI) ang -= TWO_PI; return r0 * llAxisAngle2Rot( llRot2Axis(r1/r0)*r0, ang*f);} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Rotation Cubic | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Spherical Cubic interpolation of r0 and r1 with fraction t. I liken to call it as SCURP <lsl> rotation rCub(rotation r0,rotation r1,rotation r2,rotation r3,float t){ // Spherical-Cubic Interpolation // r0 = Start, r1 = End, r2 and r3 affect path of curve! return rLin( rLin(r0,r1,t), rLin(r2,r3,t), 2*t*(1-t) );} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Vector List
Vector List, Linear | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Interpolates between two vectors in a list of vectors. <lsl> vector pLin(list v, float t, integer Loop ){ float l = llGetListLength(v); t *= l-1;
float f = (float)llFloor(t);
integer i1 = 0; integer i2 = 0;
if(Loop){ i1 = (integer)(f-llFloor(f/l)*l);
++f;i2 = (integer)(f-llFloor(f/l)*l);}
else {
if( f > l-1 ) i1 = (integer)l-1;
else if( f >= 0 ) i1 = (integer)f;
if(f+1 > l-1 ) i2 = (integer)l-1;
else if(f+1 >= 0 ) i2 = (integer)f+1; }
vector v1 = llList2Vector(v, i1);
vector v2 = llList2Vector(v, i2);
return vLin( v1, v2, t-f );}
</lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
|
Speed Controlled
Rotation Cosine Aim | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Spherical Cosine interpolation of r0 and r1 with speed regulation. Does the entire animation loop to rotate between r0 to r1 with a specific speed, with the cosine interpolation it makes it appear to accelerate and deccelerate realistically. <lsl> rCosAim( rotation r0, rotation r1, float speed ){ float ang = llAngleBetween(r0, r1) * RAD_TO_DEG;
if( ang > PI) ang -= TWO_PI;
float x; float y = (ang/speed)/0.2;
for( x = 0.0; x < y; x += 1.0 )
llSetRot( rCos( r0, r1, x/y ) );
} </lsl>
By Nexii Malthus
| ||||||||||||||||||
Old non-documented Library
Changes/ 1.0-1.1 - Added rotation types 1.1-1.2 - Added Hermite for float and vector
<lsl> //===================================================// // Interpolation Library 1.2 // // "May 12 2008", "6:16:20 GMT-0" // // Copyright (C) 2008, Nexii Malthus (cc-by) // // http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/ // //===================================================//
float fLin(float v0, float v1,float t){
return v0*(1-t) + v1*t;}
float fCos(float v0,float v1,float t){
float F = (1 - llCos(t*PI))/2; return v0*(1-F)+v1*F;}
float fCub(float v0,float v1,float v2,float v3,float t){
float P = (v3-v2)-(v0-v1);float Q = (v0-v1)-P;float R = v2-v0;float S = v1; return P*llPow(t,3) + Q*llPow(t,2) + R*t + S;}
float fHem(float v0,float v1,float v2,float v3,float t,float tens,float bias){
float t2 = t*t;float t3 = t2*t;
float a0 = (v1-v0)*(1+bias)*(1-tens)/2;
a0 += (v2-v1)*(1-bias)*(1-tens)/2;
float a1 = (v2-v1)*(1+bias)*(1-tens)/2;
a1 += (v3-v2)*(1-bias)*(1-tens)/2;
float b0 = 2*t3 - 3*t2 + 1;
float b1 = t3 - 2*t2 + t;
float b2 = t3 - t2;
float b3 = -2*t3 + 3*t2;
return ( b0 * v1+b1 * a0+b2 * a1+b3 * v2 );}
vector vLin(vector v0, vector v1,float t){
return v0*(1-t) + v1*t;}
vector vCos(vector v0,vector v1,float t){
float F = (1 - llCos(t*PI))/2; return v0*(1-F)+v1*F;}
vector vCub(vector v0,vector v1,vector v2,vector v3,float t){
vector P = (v3-v2)-(v0-v1);vector Q = (v0-v1)-P;vector R = v2-v0;vector S = v1; return P*llPow(t,3) + Q*llPow(t,2) + R*t + S;}
vector vHem(vector v0,vector v1,vector v2,vector v3,float t,float tens,float bias){
float t2 = t*t;float t3 = t2*t;
vector a0 = (v1-v0)*(1+bias)*(1-tens)/2;
a0 += (v2-v1)*(1-bias)*(1-tens)/2;
vector a1 = (v2-v1)*(1+bias)*(1-tens)/2;
a1 += (v3-v2)*(1-bias)*(1-tens)/2;
float b0 = 2*t3 - 3*t2 + 1;
float b1 = t3 - 2*t2 + t;
float b2 = t3 - t2;
float b3 = -2*t3 + 3*t2;
return ( b0 * v1+b1 * a0+b2 * a1+b3 * v2 );}
rotation rLin(rotation r0,rotation r1,float t){
// Spherical-Linear Interpolation float ang = llAngleBetween(r0, r1); if( ang > PI) ang -= TWO_PI; return r0 * llAxisAngle2Rot( llRot2Axis(r1/r0)*r0, ang*t);}
rotation rCos(rotation r0,rotation r1,float t){
// Spherical-Cosine Interpolation float f = (1 - llCos(t*PI))/2; float ang = llAngleBetween(r0, r1); if( ang > PI) ang -= TWO_PI; return r0 * llAxisAngle2Rot( llRot2Axis(r1/r0)*r0, ang*f);}
rotation rCub(rotation r0,rotation r1,rotation r2,rotation r3,float t){
// Spherical-Cubic Interpolation // r0 = Start, r1 = End, r2 and r3 affect path of curve! return rLin( rLin(r0,r1,t), rLin(r2,r3,t), 2*t*(1-t) );}
default{state_entry(){}}
</lsl>